Need Geotech Companies Near Me? Get Fast Results
Find top-rated geotech companies near you for expert soil testing, site analysis, and foundation solutions. Get reliable services tailored to your needs.
Geotechnical CMT services are focused on investigating and understanding site-specific soil, groundwater, and rock properties to support sound engineering decisions. Core services include:
geotechnical engineering services
subsurface soil investigation
foundation design recommendations
construction site soil testing
geotechnical report for construction
geotechnical drilling services
soil compaction and stability analysis
Subsurface investigations (borings, test pits, SPT sampling)
Soil classification and laboratory testing (Atterberg limits, moisture-density, permeability)
Bearing capacity and settlement analysis
Slope stability and retaining wall evaluations
Shallow and deep foundation recommendations
Geotechnical reports for permitting and design
These investigations provide critical data to architects, civil engineers, and structural designers, helping them optimize foundation systems and mitigate issues such as soil expansion, liquefaction, and groundwater intrusion.
Find top-rated geotech companies near you for expert soil testing, site analysis, and foundation solutions. Get reliable services tailored to your needs.
Geotechnical site investigations play a crucial role in the design and performance of smart buildings, as they provide essential data about the subsurface conditions that can significantly influence structural integrity, sustainability, and overall functionality. Understanding the geological and hydrological characteristics of a site is fundamental for architects, engineers, and developers, particularly when integrating advanced technologies and sustainable practices into building designs. By conducting thorough geotechnical investigations, stakeholders can identify potential challenges and opportunities that may arise from the unique characteristics of the site, thereby informing the design process and enhancing the performance of smart buildings.
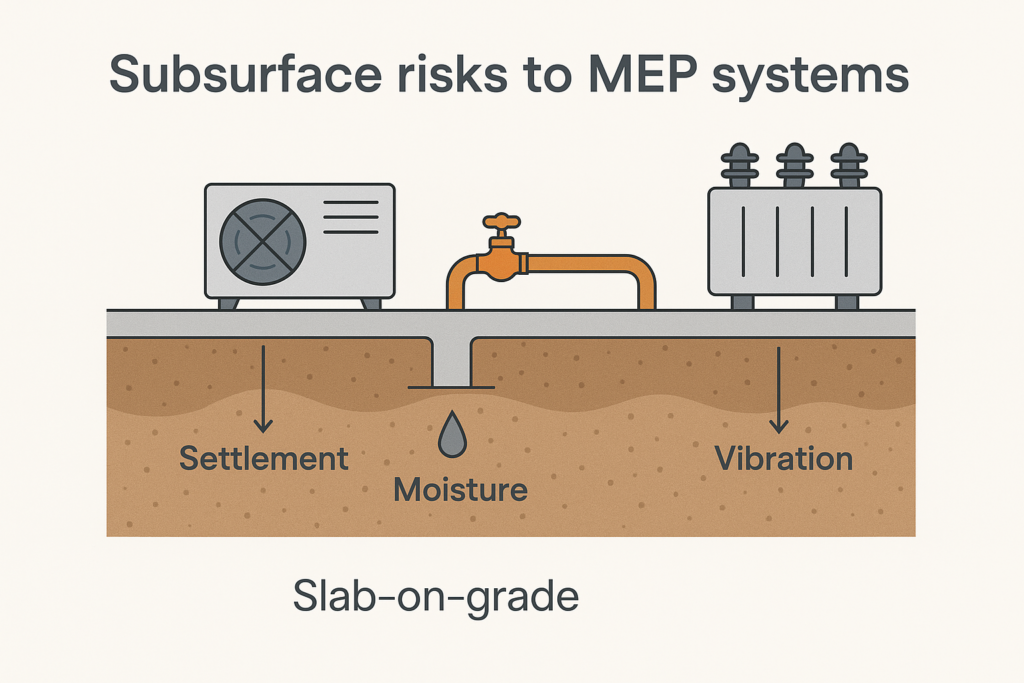
To begin with, geotechnical investigations typically involve a series of tests and analyses aimed at assessing soil properties, rock formations, groundwater levels, and other subsurface conditions. These investigations often include drilling boreholes, collecting soil samples, and performing in-situ tests to evaluate the physical and mechanical properties of the materials present. The data gathered from these investigations is invaluable, as it allows designers to make informed decisions regarding foundation design, material selection, and construction methods. For instance, if the investigation reveals weak or unstable soil conditions, engineers may opt for deep foundations or specialized techniques to ensure the building’s stability and longevity.
Moreover, the impact of geotechnical investigations extends beyond mere structural considerations. In the context of smart building design, where energy efficiency and environmental sustainability are paramount, understanding the site’s geotechnical characteristics can lead to innovative solutions that minimize resource consumption and reduce the building’s carbon footprint. For example, knowledge of local soil types and groundwater conditions can inform the design of effective stormwater management systems, which are essential for mitigating flooding and enhancing water quality. Additionally, this information can guide the implementation of geothermal heating and cooling systems, which rely on the thermal properties of the ground to optimize energy use.
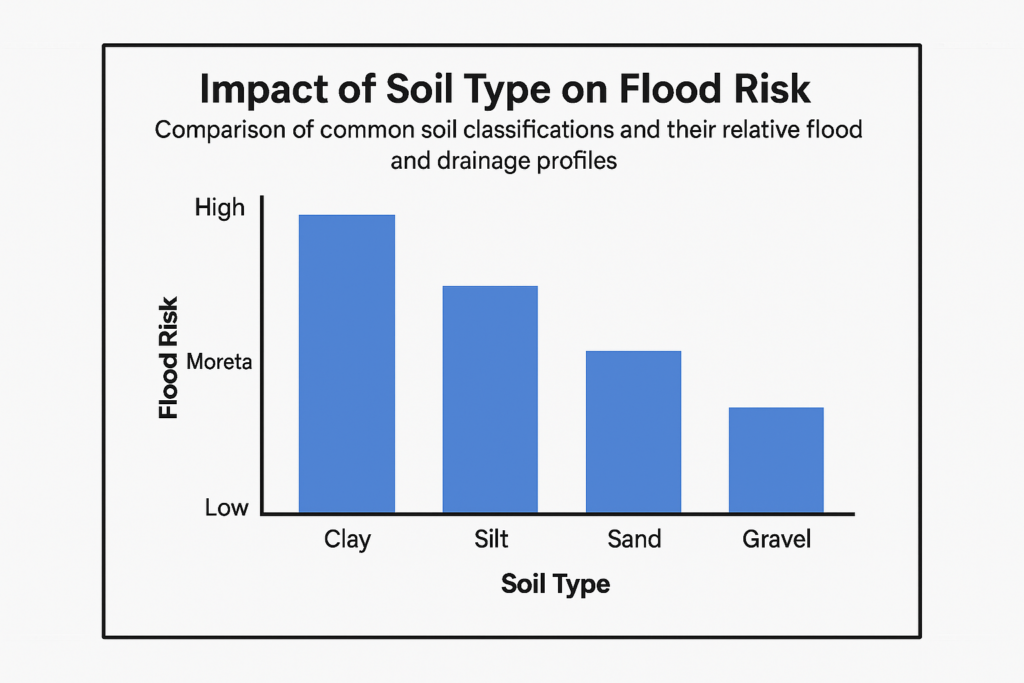
Furthermore, the integration of geotechnical data into the design process fosters collaboration among various stakeholders, including architects, civil engineers, and environmental consultants. By sharing insights gained from geotechnical investigations, these professionals can work together to develop holistic design strategies that address both structural and environmental challenges. This collaborative approach not only enhances the performance of smart buildings but also promotes resilience against natural hazards, such as earthquakes and flooding, which are increasingly relevant in today’s changing climate.
In addition to improving design outcomes, geotechnical investigations also play a vital role in risk management. By identifying potential geotechnical hazards early in the design process, stakeholders can develop mitigation strategies that reduce the likelihood of costly delays and unforeseen complications during construction. This proactive approach not only safeguards the project’s budget and timeline but also contributes to the overall success of the smart building initiative.
In conclusion, the significance of geotechnical site investigations in the context of smart building design cannot be overstated. By providing critical insights into subsurface conditions, these investigations inform foundational decisions, enhance sustainability efforts, and foster collaboration among design professionals. As the demand for smart buildings continues to grow, the integration of comprehensive geotechnical data will be essential for ensuring that these structures not only meet the needs of their occupants but also contribute positively to the environment and community at large. Ultimately, prioritizing geotechnical coordination in the design process will lead to smarter, safer, and more sustainable buildings that stand the test of time.

CMT
10665 Richmond Ave, Ste 190
Houston, Texas 77042
Mon-Fri: 7am – 6pm
Sat: 8am – 5pm
Sun: Closed
Email: [email protected]
Phone: (832) 464-8334
Geotechnical engineering, or geotech, focuses on soil and rock behavior for construction projects, ensuring stability and safety through expert analysis.
CMT Services by Construction Materials Testing (CMT) services are essential for ensuring the safety, durability, and compliance of any project site—whether it’s a towering high-rise, a highway expansion, or a industrial development.
Our certified technicians and seasoned engineers don’t just follow the standards—they challenge them, bringing precision, innovation, and a passion for quality to every test and inspection. We thrive on pushing boundaries and solving complex site challenges with clarity and confidence. To help you better understand how CMT fits into your project, we’ve answered some of the most frequently asked questions below.
Yes. We offer:
•Mobile labs or jobsite trailers
•Satellite curing facilities
•On-site CMT services for testing on fast-paced projects
Yes. We maintain:
•Scalable field and lab technician teams
•Redundant equipment for surge capacity
•Regional support to ensure uninterrupted coverage
CMT services are Available 24/7, including:
•Night pours or weekend shifts
•Emergency mobilization
•Remote and rural site coverage
•All test data is digitally archived with metadata
•Secure cloud-based storage or internal servers
•Easily retrievable for project closeouts, litigation, or QA audits
•Preliminary results: often same-day (e.g., slump test, field density)
•Final reports: typically within 24–48 hours
•Results are sent via email or uploaded to client portals
Yes. We can:
•Export PDF or Excel reports
•Integrate with systems like Procore, e-Builder, or SharePoint
•Set up automated report distribution
Cores are drilled from the pavement, trimmed, and weighed. Density is calculated and compared to design or target compaction specs.
•Marshall: Stability, flow, density, air voids
•Superpave (Gyratory Compactor): VMA, VFA, binder content, aggregate gradation
•Performance tests (rutting, cracking) may also be included
•Density: Core samples (ASTM D2726) or nuclear gauge
•Thickness: Measured directly from extracted core depths

Sieve analysis (ASTM C136) determines the particle size distribution of soils or aggregates. It’s crucial for assessing gradation for concrete, asphalt, or base materials.
Sieve analysis (ASTM C136) determines the particle size distribution of soils or aggregates. It’s crucial for assessing gradation for concrete, asphalt, or base materials.
•Standard Proctor (ASTM D698): Simulates light compaction
•Modified Proctor (ASTM D1557): Uses higher energy to simulate heavy compaction, commonly used for roadway embankments
Using a nuclear density gauge (ASTM D6938) to measure:
•Dry density
•Moisture content
Results are compared against Proctor values to determine percent compaction.
Typically:
•Average of 3 consecutive tests: ≥ f’c (design strength)
•Individual tests: no more than 500 psi below f’c for strengths > 5000 psi
•Projects may have stricter tolerances.
•7-day breaks: within 24 hours after the 7th day
•28-day breaks: within 24–48 hours after the 28th day
Same-day reporting is often available upon request.
Per ASTM C39, cured cylinders are placed in a hydraulic testing machine and loaded until failure. The max load is divided by the cross-sectional area to determine compressive strength.
Cylinders are cast in standard 6”x12” molds per ASTM C31. They’re stored in a curing box on-site for initial 24 hours, then transported to a lab for curing at 73°F ±3°F until break testing.
Cylinders are cast in standard 6”x12” molds per ASTM C31. They’re stored in a curing box on-site for initial 24 hours, then transported to a lab for curing at 73°F ±3°F until break testing.
•Immediate notification to the client/engineer
•Retesting or resampling if needed
•Non-conformance reports (NCRs)
•Root cause analysis and recommendations
Yes, we provide standardized test report templates with:
•Sample ID, test type, method
•Results, specifications, remarks
•Technician and reviewer signatures
Complies with individual ASTM recommendations
Based on:
•Project specifications
•Contract documents
•DOT or industry standards
•Engineer or owner’s quality control plan
•Concrete: Slump, air content, unit weight, temperature, compressive strength
•Soil: Proctor density, Atterberg limits, sieve analysis, field density (nuclear gauge)
•Asphalt: Core density, Marshall/Superpave, binder content, gradation
•Aggregates: Sieve analysis, specific gravity, absorption, LA abrasion
Yes, all tests are performed to standards recognized by local, state, and federal agencies, including DOTs, municipalities, and regulatory authorities.
Yes, we participate in:
•AASHTO re:source proficiency sample programs
•CCRL inspections
•USACE – United States Corp of Engineers
•State DOT accreditations ensures quality and consistency.
Labs are certified through programs like A2LA, AASHTO Accreditation and CCRL.
Technicians hold certifications such as:
•ACI Concrete Field Testing Technician
•NICET (Soils, Asphalt)
•WAQTC or state DOT certifications
We follow industry-recognized standards, including:
•ASTM International (e.g., ASTM C39 for concrete compression)
•AASHTO standards (common in DOT work)
•Project-specific specs (TxDOT, FAA, Army Corps, etc.)
Testing occurs throughout the project lifecycle:
•Pre-construction: material submittals and mix designs
•During construction: field sampling and lab testing
•Post-construction: final testing for as-builts and quality verification
A certified third-party testing agency typically performs the tests, though sometimes the contractor or the owner hires the testing firm. Engineers and inspectors review results for compliance.
Common materials include:
•Concrete (compressive strength, air content, slump)
•Soil (compaction, classification, density)
•Asphalt (density, gradation, binder content)
•Aggregates (sieve analysis, specific gravity)
•Steel/Rebar (tensile strength, bend tests)
Construction Material Testing (CMT) ensures that the materials used in construction (concrete, soil, asphalt, steel, etc.) meet required quality, strength, and performance standards. It helps verify compliance with project specifications and ensures long-term structural integrity and safety.